Biochemical Cycles , problems that our environmental microbes facing and their solutions
|
Biochemical Cycles ,
problems that our environmental microbes facing and their solutions
|
Biochemical Cycles
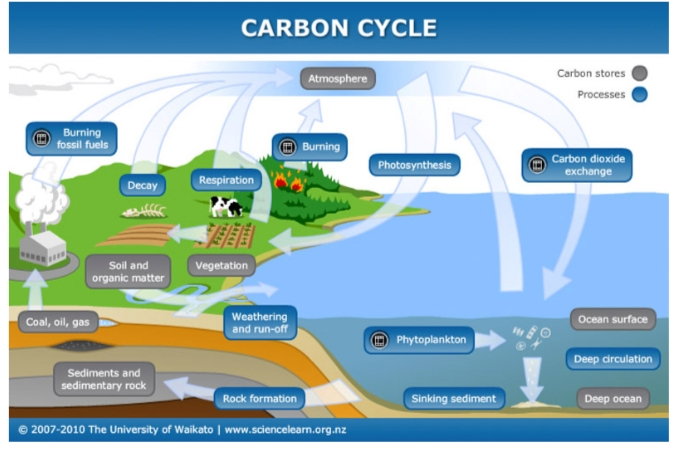
Carbon Cycle:
- · There are many important processes in the carbon cycle that primarily relate to photosynthesis, decomposition, and deposition.
- · CO2 is absorbed by various plants and vegetation and converted into carbohydrates via photosynthesis.
- · Carbon travels through the food chain and eventually makes it away into the atmosphere via cellular respiration, burning of fossils or decay of organisms.
- · Carbon travels from ground to atmosphere.
- · Fixation of carbon is carried out by living organisms including plants and animals.

Figure 1Carbon Cycle
Nitrogen Cycle:
- · It has the processes of mineralization, nitrification, and denitrification.
- · Nitrogen fixation occurs from converting Nitrogen gas (N2) into Ammonia (NH3).
- · Nitrogen is sent to the ground.
- · The nitrogen cycle takes place in Earth’s various spheres (geosphere, atmosphere and biosphere).
- · All stages of the nitrogen cycle are carried out by microorganisms.
- · Similarities in between Nitrogen and Carbon Cycle:
- · Both are biochemical cycles that release their respective elements into the atmosphere.
- · The carbon and nitrogen cycles work together and can often be referred as the CNO cycle.
- · Both start as a gas and end as a gas.

Figure 2 Nitrogen Cycle
Issues that our environment faces:
Some of the major issues that our ecosystem and fresh water microbes’ faces are;
1) Emission
of Carbon
2) Emission
of Nitrogen
3) Conservation
of water
Dealing with the issues:
Reduce the Nitrogen emission:
N2 emission can be reduced by making process changes such as modification to the combustion process or by installing air pollution control equipment such as selective non_ catalytic reduction (SNCR) or selective catalytic reduction (SCR)
§ Use
less nitrogen fertilisers
§ Use
split applications of nitrogen fertilisers
§ Use
legume crops or pastures in the rotation instead of nitrogen fertilisers
§ Use
minimum tillage of cropping
§ Prevent
waterlogging
§ Use
nitrification inhibitors
§ Use
of retard injection
§ Use
of fuel nozzle modification
§ Change
of compression ratio
Reduce the Carbon emission:
We can control the emission of carbon by planting trees more and more in our surroundings. Minimize driving by setting concrete reduction goals and walking, biking, carpooling and using public transit as much as possible.
§ Minimize
purchase of new products, especially resource intensive or heavily packaged
products.
§ Embrace
a minimalist life style.
§ Reduce
energy use; seal your heating and cooling ducts.
§ Buy
energy efficient office equipment.
§ Switch
to LED light bulbs
§ Minimize
use of fireplaces or wood stoves
§ Use
less Hot water
§ Drive
less and drive smart
§ Buy
energy efficient products
Conservation of water:
We should have to start from our self and our homes first, when running a bath, plug the bathtub before turning on the faucet.
§ Better
yet, take only 5 minutes of shower instead of bath it saves 70 gallons of water
§ Turn
off the water while brushing your teeth and can save up to four gallons per minutes
§ Add
food colouring to check the leaks in toilet
§ Clean
driveways and sidewalks with broom instead of hose
§ Raise
awareness of the importance of water
§ Install
water efficient devices at institutes
§ To
save water in school, install aerators and water efficient plumbing fixtures
§ Avoid
flushing the toilet unnecessarily
§ Landscapes
with native, drought tolerant plants, and mulch regularly
§ Encourage
students to use refillable water bottle and educate them to pour leftover water
into garden
|
TIPS ON WATER CONSERVATION
|
|
|
Put the signs near the basin
|
Turn
off the water while brushing your teeth and can save up to four gallons per
minutes
|
|
Raise
awareness of the importance of water
|
Install
water efficient devices at institutes
|
|
Install aerators and water efficient plumbing fixtures
|
Find and repair leaks
|
|
Figure 3Conservation of Water
|

Great 👌 keep it up
ReplyDeleteThank you @Iqra
Delete